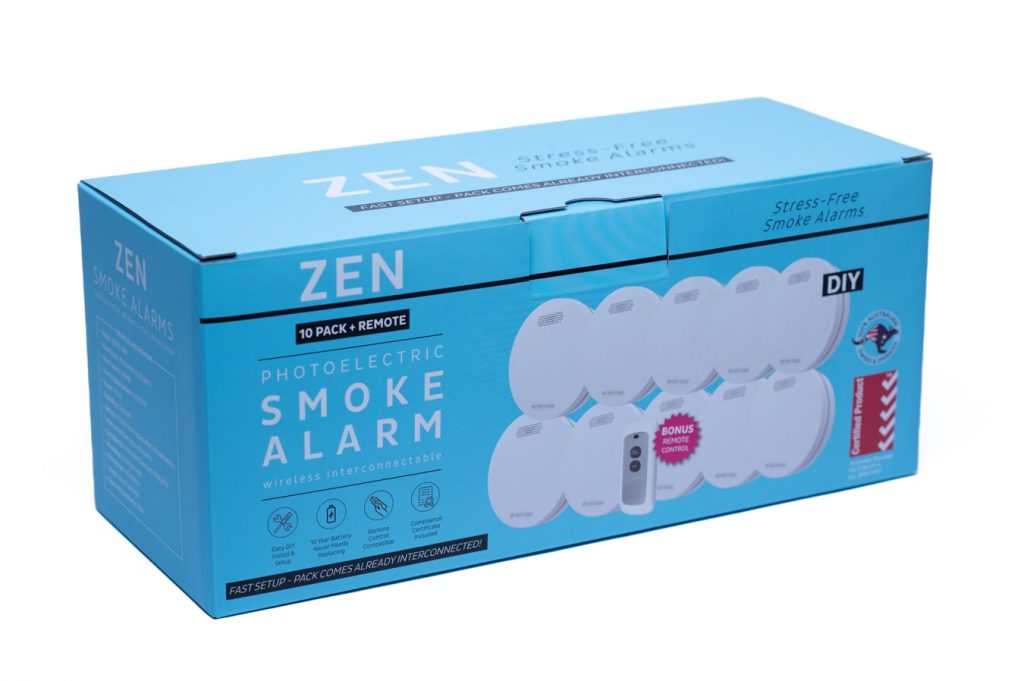
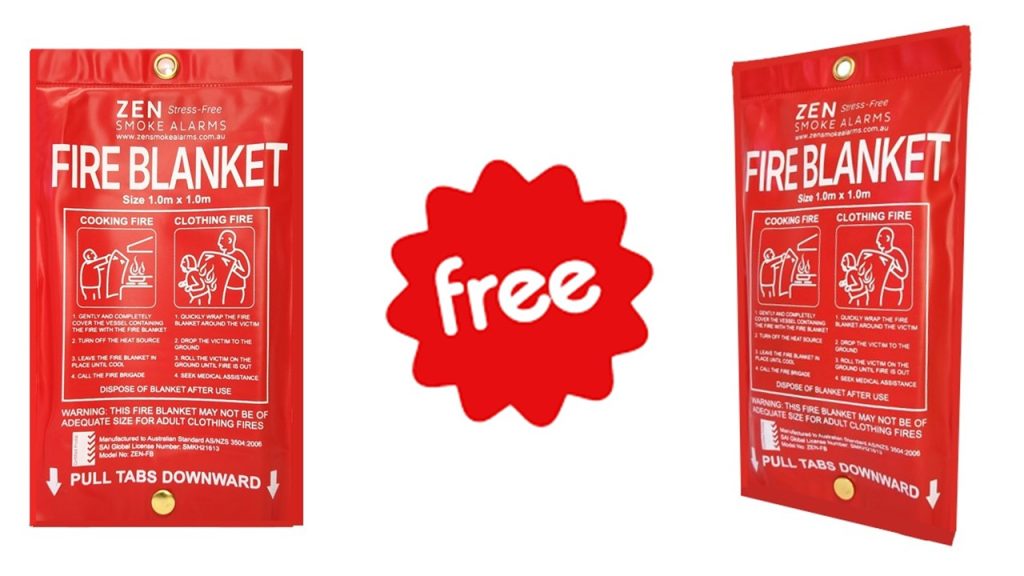
Fire prevention and preparedness are paramount in your home. In addition to the early fire warning provided by your ZEN smoke alarms, there is another hero in the toolkit of safety measures: the humble ZEN fire blanket. This unassuming yet highly effective tool can make a significant difference in protecting both your home and loved ones in the event of a fire emergency.
ZEN Fire Blanket – Immediate Action, Minimal Effort!
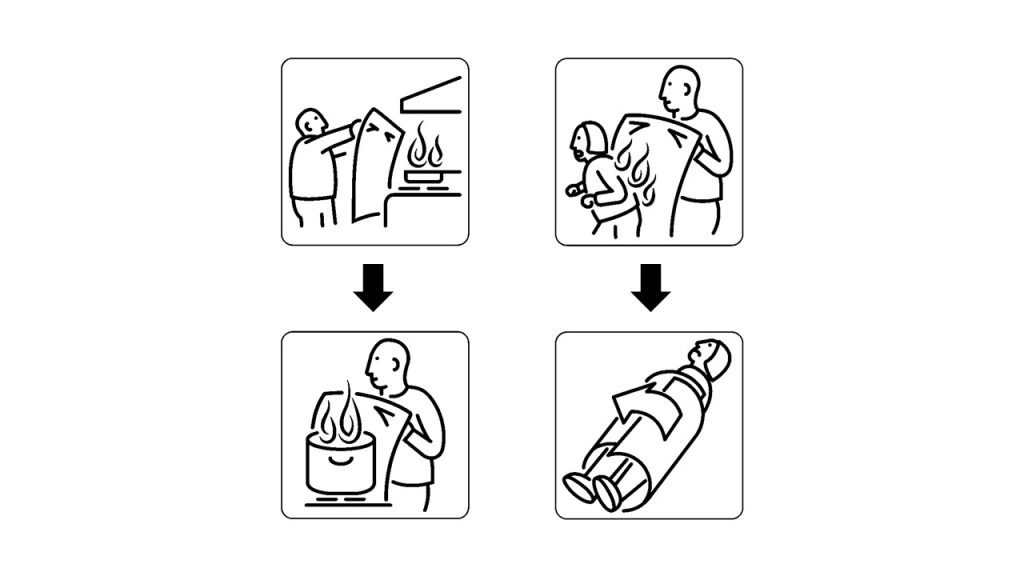
Imagine a small kitchen fire erupts from a stovetop mishap – a greasy frypan suddenly ignites, sending panic through the air. This is when the ZEN fire fire blanket shines. Unlike a fire extinguisher that requires knowledge of operation and can potentially spread the fire if not used correctly, a fire blanket simply requires you to grab it and place it gently over the flames. The fire is quickly smothered as the blanket starves it of oxygen, effectively extinguishing it with minimal effort, and preventing it from spreading.
Fire Blankets Are Simple And Easy To Use
One of the greatest advantages of the ZEN fire blanket is its simplicity. Designed to be user-friendly even in stressful situations, it doesn’t involve any complex mechanisms or technical knowledge. Simply pull down on the quick-release tabs and the ZEN fire blanket slides out from its protective pouch and is ready to use. This makes it ideal for everyone in the household, including children and elderly family members who may find fire extinguishers intimidating or difficult to operate.
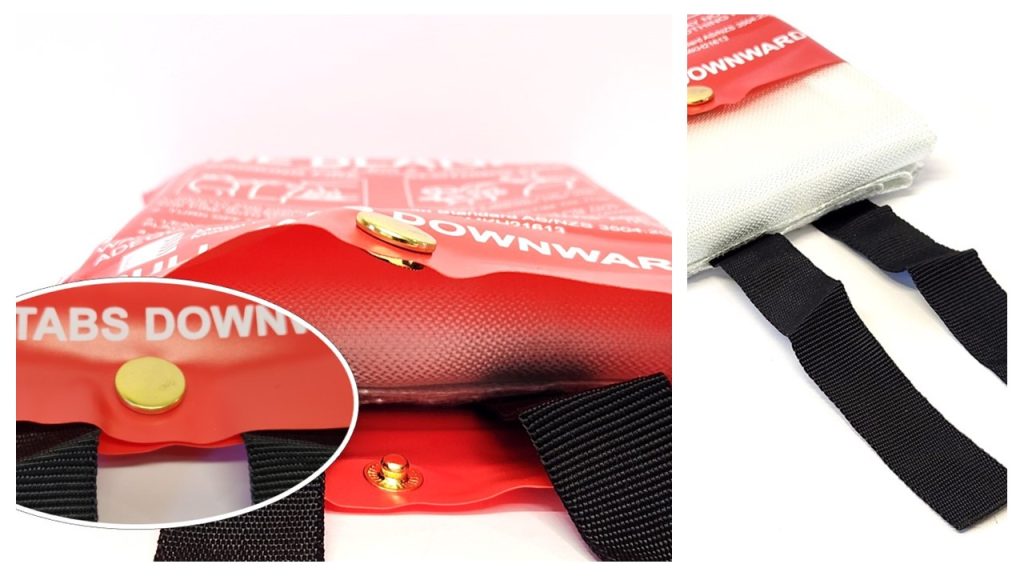

Versatility In Application
While commonly associated with kitchen fires, fire blankets are versatile and can be used in other various scenarios. They are effective not only on stovetop fires but also on BBQ fires or fires caused by accidents around the home. Having a fire blanket means you’re prepared for these unpredictable moments, giving you confidence in your ability to respond to emergencies. In addition to the kitchen, you may also consider installing a fire blanket in the following locations; outdoor BBQ area, caravan, garage, car, workshop, boat, home office, backyard shed, carport or granny flat.
Receive Your FREE ZEN Fire Blanket Today!
For a limited time, every ZEN photoelectric smoke alarm bundle pack (5-pack, 7-pack, 10-pack) will automatically receive a free ZEN fire blanket (in addition to the bonus smoke alarm remote control). The ZEN fire blanket perfectly complements the ZEN interconnected smoke alarm range – level up your home protection today!

Peace Of Mind
A ZEN fire blanket provides peace of mind, additional to your ZEN smoke alarms. It’s a proactive step towards ensuring the safety of your household, and empowers you to take action in the face of a fire emergency. Knowing you have a fire blanket readily accessible helps alleviate anxiety and instills a sense of confidence that you’re prepared for the unexpected.

Fire Blanket Conclusion
Whilst we all hope to never face a fire emergency, preparedness is key to safeguarding our homes and loved ones. A ZEN fire blanket stands as a reliable ally in this mission, offering simplicity, effectiveness, and peace of mind—all packed into a compact, easily accessible tool. Consider adding a ZEN fire blanket to your ZEN interconnected smoke alarm arsenal; it’s a small investment that can yield valuable protection when every second counts.

Want to know more? Watch our ZEN quick-start video or call us on 0478 596 402
We love talking smoke alarms! (and fire blankets)